
Based on an idea for problem-solving developed earlier in the 20 th century, Ishikawa’s diagram because popular in the 1960s at Kawasaki. Ishikawa invented the Fishbone Diagram for the shipbuilding industry in Japan. The use of a Fishbone Diagram requires that a team look at all possible causes for errors and mistakes, not just those they have come up with in the past or that team members suspect is the root cause.īecause of its usefulness, a Fishbone Diagram is one of the most popular tools in Six Sigma. It’s also useful for teams who find that their thinking on solving a challenge has fallen into a rut.

Another name for the diagram is the Cause and Effect Diagram or Ishikawa Diagram (named for the diagram’s inventor, Kaoru Ishikawa).Ī Fishbone Diagram is an effective tool for project teams tasked with finding the root causes of a problem. More information on the practical application of the Ishikawa diagram is presented during dedicated training courses on the 8D and Kaizen methodology, to which we cordially invite you.A Fishbone Diagram is a visual tool that allows project teams to easily display a list of potential causes of a problem, then break these causes down into increasingly more detailed components until a link is found between a root cause and the final outcome.
#Ishikawa diagram kaizen verification#
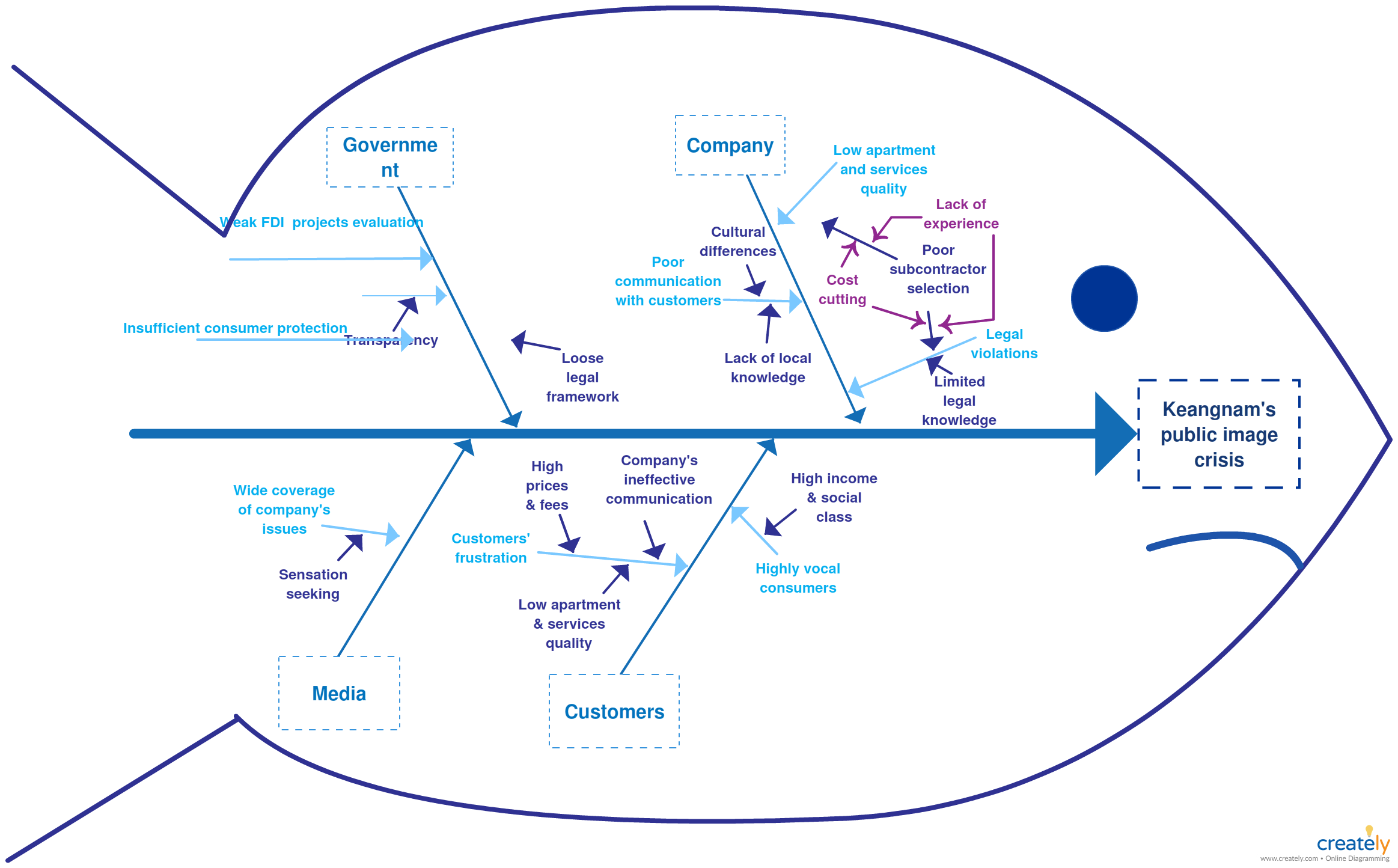
Kaizen methodology – with this approach, is used as 4M (Man, Machine, Method, Material) or 4M + 1D (Design).

8D reports in step D4 – root cause analysis.Most often, we can deal with it when using: Usually it’s used in the quality area, but it can also be successfully carried out in logistic, health and safety (ergonomics, accidents at work, etc.) and production analysis. Ishikawa Diagram, also known as the “fishbone”, is a qualitative tool that is often used during problem solving by the production plant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
